Types of digital computers
In the ever-evolving landscape of technology, digital computers play a pivotal role in shaping our modern world. These devices come in various forms, each designed to cater to specific needs and applications. In this blog, we will delve into the diverse realm of digital computers, exploring the different types that exist and their unique functionalities. The world of digital computers is vast and diverse, encompassing machines ranging from the pocket-sized smartphones we carry to the room-sized giants powering scientific research. But how do we categorize these seemingly disparate devices? This blog delves into the different types of digital computers based on their size, processing power, and typical applications
Personal Computers (PCs)
-
Personal Computers, commonly known as PCs, are the most ubiquitous type of digital computer. Found in homes, offices, and educational institutions, PCs are designed for individual use. They come in various forms, including desktops, laptops, and even compact form factors like mini PCs. Personal Computers are versatile and can perform a wide range of tasks, from word processing to gaming and multimedia editing.

Microcomputers
-
These are the most familiar computers to most people, encompassing personal computers (PCs), laptops, tablets, and smartphones. They are compact, relatively affordable, and offer enough processing power for everyday tasks like browsing the web, working on documents, and running basic software
Minicomputers
-
Once widely used for business applications, minicomputers occupy a niche between microcomputers and larger systems. They are more powerful than microcomputers and can support multiple users simultaneously, making them suitable for tasks like managing databases or running server applications in small businesses


Workstations
-
Workstations are powerful computers designed for specialized tasks such as graphics design, 3D modeling, and scientific simulations. These machines often boast high-performance hardware, including advanced processors, large amounts of RAM, and high-end graphics cards. Workstations cater to professionals who require enhanced computing power for demanding applications.
Servers
-
Servers form the backbone of the internet and networked systems. These computers are designed to handle and process requests from other computers, known as clients. Servers come in various types, including web servers, database servers, and file servers. They are crucial for hosting websites, managing data, and facilitating communication between devices.
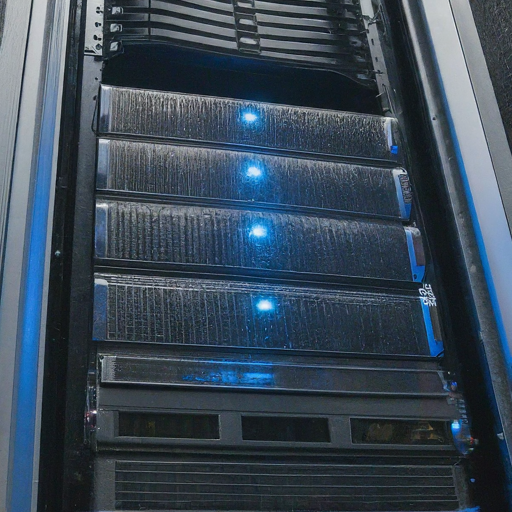


Mainframes
-
Mainframes are large-scale computers optimized for handling massive amounts of data and transactions. Commonly used in enterprises and organizations, mainframes ensure reliable and secure data processing. They excel in tasks such as financial transactions, airline reservations, and other mission-critical applications that demand high reliability and processing power.
Supercomputers
-
Supercomputers are at the forefront of computational power and are used for complex scientific and engineering simulations. These machines are capable of executing trillions of calculations per second, enabling researchers to tackle intricate problems in fields like weather modeling, molecular dynamics, and nuclear simulations. Supercomputers are often built using parallel processing techniques to achieve exceptional computational speeds.


Embedded Computers
-
Embedded computers are specialized systems integrated into other devices to control specific functions. Commonly found in household appliances, automobiles, and industrial machinery, embedded computers operate silently in the background, ensuring the smooth functioning of the larger system.
Quantum Computers
-
Quantum computers represent the cutting edge of computing technology. Leveraging the principles of quantum mechanics, these computers can perform complex calculations at speeds unattainable by classical computers. While still in the experimental stage, quantum computers hold the potential to revolutionize fields such as cryptography, optimization problems, and drug discovery.

Conclusion
The world of digital computers is vast and varied, with each type serving a specific purpose and contributing to the overall advancement of technology. Whether you’re using a personal computer for everyday tasks or a supercomputer for research, understanding the different types of digital computers allows us to appreciate the diversity of computing technology and its impact on our lives. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more innovation and new types of digital computers to emerge, shaping the future of computing.



